Cardiology Care
Cardiology is the study and treatment of disorders of the heart and the blood vessels. A person with heart disease or cardiovascular disease may be referred to a cardiologist.
Cardiology is a branch of internal medicine. A cardiologist is not the same as a cardiac surgeon. A cardiac surgeon opens the chest and performs heart surgery.
A cardiologist specializes in diagnosing and treating diseases of the cardiovascular system. The cardiologist will carry out tests, and they may some do procedures, such as heart catheterizations, angioplasty, or inserting a pacemaker.
Heart problems relate specifically to the heart, while cardiovascular disease affects the heart, the blood vessels, or both.
The AHC provides service to
Cardiac disorders such as coronary heart disease, including myocardial infarction, heart failure, cardiomyopathy, and arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation, are common and are a major cause of mortality in elderly people
At your first visit to a cardiologist you will get a thorough review of your medical history and assessment of risk factors of coronary artery disease. Blood pressure, heart rate and electrocardiogram will be obtained. … The cardiologist will review the data with you and answer all your cardiac questions or concerns.
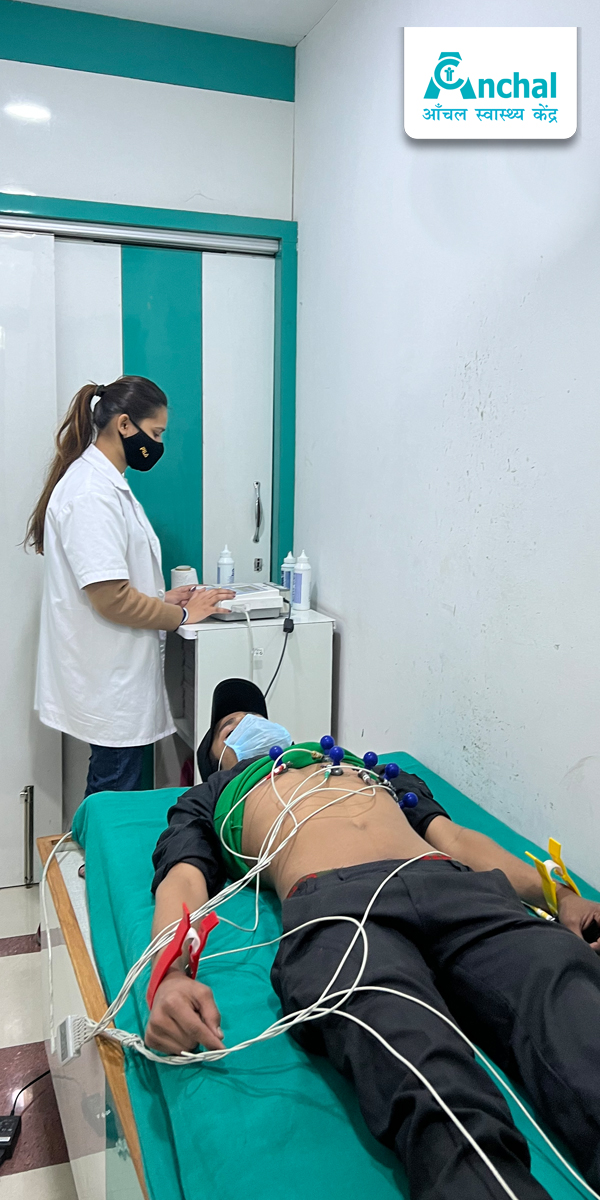
The equipment in a Cath lab allows the doctor to see the state of the heart. Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): this records the electrical activity of the heart. Ambulatory ECG: this records heart rhythms while the person carries out exercise or their regular activities.
Blood pressure
Blood pressure is an important measurement that can be taken by your doctor, nurse or healthcare assistant. It’s recorded as two readings:
- systolic pressure (higher reading) – this records the pressure within the blood vessels as the heart contracts and forces blood out into the arteries
- diastolic pressure (lower reading) – this records the pressure when the heart fills up with blood again
Echocardiogram
An echocardiogram – or “echo” – is an ultrasound scan of the heart. It uses high frequency sound waves to create an image of your heart.
This is a painless procedure that is usually performed in hospital or in an outpatient clinic. You’ll have jelly applied to your bare chest, and an experienced operator will move the probe around your chest to get good views of your heart.
It can check:
- the size of the heart
- how well the heart muscle is contracting and relaxing
- how well the valves are working
Electrocardiogram
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a test that records the electrical activity of the heart. The ECG reflects what’s happening in different areas of the heart and helps identify any problems with the rhythm or rate of your heart. The ECG is painless and takes around 5-10 minutes to perform.
24-hour or ambulatory electrocardiogram
In this test, electrodes are connected to a small box and attached to a belt. You wear this belt for 24 hours, as you go about your normal daily activities. The ECG will be monitoring and will be able to record any abnormalities over the day. You’ll also be asked to record any symptoms. Then this can be assessed by the electrophysiologist or cardiologist.
Stress test
This stress test – or exercise tolerance test (ETT) or treadmill test – is similar to an ECG but records the activity of the heart as it works harder, for example while you’re walking on a treadmill. This “exercise” ECG records how the heart responds to exercise.
Tilt test
A tilt test allows the doctor to monitor your blood pressure and heart rate when you’re lying down and standing up.
This test is designed to assess symptoms you may have been experiencing, like light-headedness or dizziness, and to see if your symptoms are related to your blood pressure or heart rate.
The test will normally be done as an outpatient appointment in an electrophysiology department.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
This painless scan uses a magnetic field inside a scanning machine to produce images of the heart and blood vessels.
It’s useful for checking problems with structure of heart and blood supply.
It’s very helpful in getting images from people whose vessels and heart anatomy are difficult to see using angiography.
Cardiac computed tomography (Cardiac CT)
Cardiac CT uses a special X-ray machine, which moves around your body and takes detailed 3-D images of your heart.
Thallium scan (myocardial perfusion scintigraphy)
This scan shows how well blood is reaching the heart muscle through your coronary arteries. A small amount of thallium (radioactive substance) is injected into a vein, and a special camera moves around your heart. The camera picks up traces of thallium and produces pictures.
As thallium doesn’t travel well to areas where there’s a poor blood supply, the pictures can be used to see how well blood is reaching your heart. It’s a useful alternative to an exercise test if this can’t be done or when specific information on your heart muscle is needed which a treadmill exercise test can’t provide.
This is done at rest and during exercise.
The very low levels of radiation used are considered to be safe.
Coronary angiogram
A coronary angiogram is a type of X-ray used to examine the coronary arteries supplying blood to your heart muscle. It’s considered to be the best method of diagnosing coronary artery disease – conditions that affect the arteries surrounding the heart.
During the test, a long, flexible tube called a catheter will be inserted into a blood vessel in either your groin or arm. The tip of the catheter will then be fed up to your heart and coronary arteries.
Special dye will then be injected through the fine catheter into your coronary arteries, and X-ray images will be taken. These images created during angiography are called angiograms.
These images will be used to identify narrowing or blockage of the arteries that may be responsible for your symptoms. This test is also sometimes required to reach a diagnosis for patients with heart valve and muscle disease.
Blood tests
There are a number of blood tests that can be done to rule out other causes of heart symptoms, and to measure different levels within the body that can affect the heart. You may also get blood tests done if you begin a new heart medicine.
The most common are:
- Full Blood count (FBC) – this test measures the levels of red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. It also measures the haemoglobin (oxygen carrying component of red blood cells).
- Urea and Electrolytes (Us and Es) – urea levels help to monitor how the kidneys are working. Electrolytes help to stabilise the heart rhythm.
- Glucose – this test measures the level of sugar in the blood.
- Liver and thyroid function – these tests measure liver function and the thyroid function.
- Troponin blood test – troponin is a protein which is released into the blood stream when the heart muscle is damaged. The troponin level provides a quick and accurate measure of any heart muscle damage. It’s used to help in the assessment following suspected heart attack. It may be taken on admission to hospital and/or 12 hours from the onset of symptoms.
- Cholesterol level and lipid profile.
- Natriuretic peptides – an indicator of heart failure.
Chest X-ray
A chest X-ray is useful for showing the size and shape of the heart and detecting chest disorders. This can provide doctors additional information about your symptoms (which can often relate to both chest and heart conditions) and can also show any fluid in the lungs, which may be caused by heart disease.
The Best and Affordable Cardiology Care in Ghaziabad
If you are searching for the top cardiology specialist for yourself or your loved ones, this might be of interest to you. Unfortunately, cardiology treatment is quite expensive, and almost 60% of the population of our country cannot afford full-fledged heart care treatment. The prerequisite level of awareness is also missing, owing to which people often fall prey to cardiac arrest and similar other issues.
At Anchal Health Centre, the leading charitable heart hospital Ghaziabad, we offer top-notch cardiology treatment to all our patients. Worry not, as we have a pool of experts who offer impeccable cardiology care Ghaziabad.
Our nominal charges and credible treatment have made us the top choice of our clients. At Anchal Health Centre, the best charitable heart hospital Ghaziabad, we believe in offering high-quality cardiology treatment to every patient without forcing them to pay hefty charges.
Connect with us for effective cardiology care, and you won’t have to spend your fortune!
For Appointment Call: 9811173783, 9911173780